Describe the Structure and Function of the Blood Brain Barrier
Astrocytes also known as astroglia or astroglial cells were discovered by scientist Karl Bergmann and were originally called Bergmann glia due to their classification as. 2015 First Sitting Paper 1 Question 3 Sakurai 2016 2015-1-3 Describe the structure and function of the blood brain barrier.
What Is Blood Brain Barrier Permeability Cusabio
The BBB at the level of brain microvessel endothelium is the major site of bloodCNS exchange.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/6720/Protective_barriers_of_the_brain.jpg)
. The structure and function of the BBB is summarised the physical barrier formed by the endothelial tight junctions and the transport. Histology of Blood Testis Barrier. The structure and function of the BBB is summarised the physical barrier formed by the endothelial tight junctions and the transport.
The blood-brain barrier BBB protects the vertebrate central nervous system from harmful blood-borne endogenous and exogenous substances to ensure proper neuronal function. The BBB at the level of brain microvessel endothelium is the major site of blood-CNS exchange. Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier The blood-brain barrier separates the cerebral capillary blood from the brains interstitial fluid.
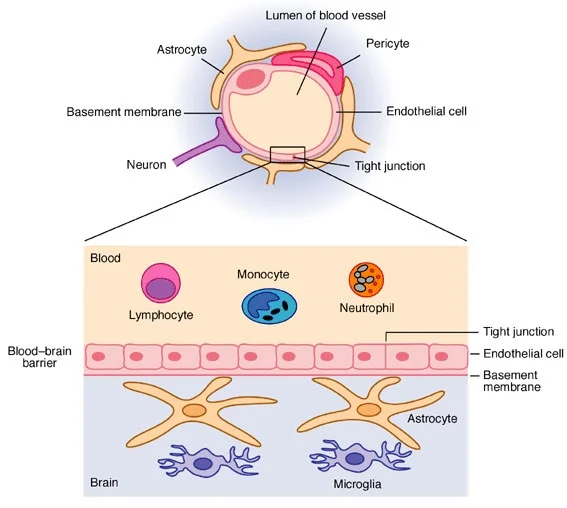
The blood-brain barrier BBB actually consists of several relatively distinct barriers operating in parallel to one another in different anatomical regions. The blood-brain barrier is made up of tightly packed cells in the brains capillaries that prevent harmful substances from entering the brain. It is formed of endothelial cells as a result of tight junctions between them.
The bloodbrain barrier BBB is a term used to describe the unique properties of the microvasculature of the central nervous system CNS. Physiology of the blood-brain barrier. This membrane the protective barrier in the brain as it prevents the entr.
Acts as a barrier in the CNS capillaries which restricts passage of substances into the CNS. Maintains a constant environment for the brain. The blood-brain barrier BBB is a diffusion barrier which impedes influx of most compounds from blood to brain.
2010 What is the blood brain barrier and describe 3 of the functions that the CNS barriers provide there are 5 provided in the article its a physiological psychology Question. While it performs an important function in keeping your brain healthy it can also cause challenges in treating some. Cells at three key interfaces form barriers between the blood and the CNS.
The BBB choroid plexus epithelium and the epithelium of the arachnoid mater functions as a physical transport metabolic and immunologic barrier. To understand the functions of blood testis barrier it would be worthy to go through a little bit about its basic anatomical structure and histology. The blood-brain barrier has several important functions that ensure a homeostatic environment within the CNS.
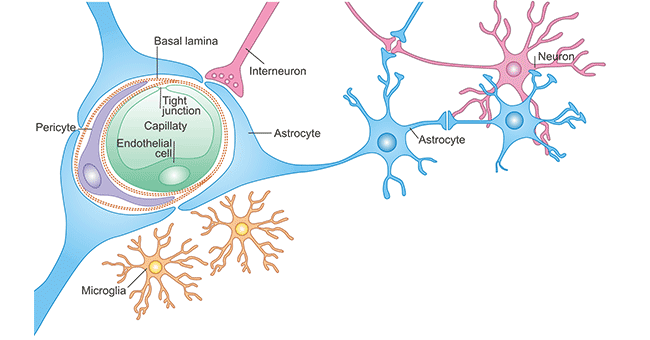
The BBB describes a function that is established by endothelial cells of CNS vessels in conjunction with pericytes astrocytes neurons and microglia together forming the neurovascular unit NVU. Cells at three key interfaces form barriers between the blood and the CNS. Tight junction This is also called the occluding junction.
CNS vessels are continuous nonfenestrated vessels but also contain a series of additional properties that allow them to tightly regulate the movement of molecules ions and cells between the blood and the CNS Zlokovic. The main function of the blood-brain barrier is to act like a filter between the blood and brain tissues selectively allowing some nutrients and molecules in while keeping the rest out. This article will look at the overall structure of the blood-brain blood-nerve and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers found throughout the nervous system.
Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. The blood-brain barrier BBB is the specialized system of brain microvascular endothelial cells BMVEC that shields the brain from toxic substances in the blood supplies brain tissues with nutrients and filters harmful compounds from the brain back to the bloodstream. The close interaction between BMVEC and other components of the neurovascular unit astrocytes.
Protects the brain from foreign substances in the blood that may injure the brain. In summary the blood-brain barrier is an important layer of cells surrounding the brain that takes in nutrients and keeps out toxins. Structure and function of.
Occludin prevents paracellular flow Lack fenestrations Lack transcellular pathways such as vescicles Selective transport proteins. This is the primary function of the blood-brain barrier. Capillary endothelial cells and basement membrane neuroglial membrane and glial podocytes.
The BBB at the level of brain microvessel endothelium is the major site of bloodCNS exchange. Structure - Mechanical barrier Endothelial cells Tight junctions between cells formed by membrain proteins eg. Protects the brain from neurotransmitters in the rest of the body.
Capillary endothelial cells are non-fenestratated and stitched together with tight junctions that are not found elsewhere in. Each of the three main CNS interface layers. An inflammation of the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord.
Three cellular elements of the brain microvasculature compose the BBB-endothelial cells astrocyte end-feet and pericytes PCs. It does so primarily by regulating the composition and volume of the cerebrospinal fluid CSF which surrounds structures within the. The BBB consists of three structures.
The blood-brain barrier is a semi-permeable membrane that prevents certain components of the blood from passing out of circulation into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system. Additionally special attention will be paid to those areas within the brain that lack a blood-brain barrier and to clinically relevant points with respect to this. Structure and Function.
The structure and function of the BBB is summarised the physical barrier formed by the endothelial tight junctions and the transport barrier resulting from membrane transporters and vesicular mechanisms. The bloodbrain barrier BBB bloodCSF barrier and the arachnoid barrier. It protects your brain from injury and disease while also letting in substances that your brain needs like oxygen and water.
It is a protein complex which provides transport of solutes and. Blood brain is a selectively permeable membrane that surrounds the blood vessels in the brain. The blood-brain barrier BBB blood-CSF barrier and the arachnoid barrier.
These barriers restrict and regulate the passage of materials between the peripheral and cerebrospinal compartments. Blood Testis Barrier is Formed by the Following Structures. Tight junctions TJs present between the cerebral endothelial cells form a diffusion barrier which selectively excludes most blood.
The barrier functions are dynamic and respond to regulatory signals from both blood and brain.
What Is The Blood Brain Barrier Brain Stuff

Comments
Post a Comment